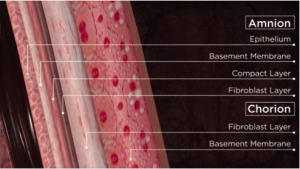
Human amniotic membrane is comprised of the innermost layer of the placenta and lines the amniotic cavity. The membrane is composed of multiple layers including a single layer of epithelial cells, a basement membrane and an avascular connective tissue matrix. The tissues of the placenta present a very complex interrelationship of materials that possess numerous physiologic characteristics, that can in turn change in importance with the appropriate stage of gestation. During pregnancy, the placenta permits the passage of nutrients, metabolites and metabolic gases, and provides physical and immunological protection to the developing fetus. In addition, it produces a variety of steroids and important metabolic hormones.
Amniotic membrane is a unique material and its composition contains collagen types I, III, IV, V, and VII. Amniotic membrane is composed of structural extracellular matrix (ECM), that also contains specialized proteins fibronectin, laminins, proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans. In addition, amniotic membrane contains essential, active, healing growth factors such as epidermal growth factor (EGF), transforming growth factor beta (TGF-b), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and platelet derived growth factor (PDGF).8 Amniotic tissues have shown little to no HLA-A, B, C antigens and β2 microglobulin.3
References:
- Niknejad H; Peirovi H; Jorjani M; Ahmadiani A; Ghanavi J; Seifalian AM “Properties of the amniotic membrane for potential use in tissue engineering.” Eur Cell Mater. (15). 01-JAN-2008. pp 88 – 99.
- Rahman I; Said DG; Maharajan VS; Dua HS “Amniotic membrane in ophthalmology: indications and limitations.” Eye. (23)10. 2009. pp 1954–1961.
- Baradaran-Rafii A; Aghayan H; Arjmand B; and Javadi M. “Amniotic Membrane Transplantation.” Iran J Ophthalmic Res. (2)1. 2007. pp 58-75.
- John, T. “Human amniotic membrane transplantation: Past, present, and future..” Ophthal Clin N Am. (16). 2003. pp 43-65.
- Adly OA; Moghazy AM; Abbas AH; Ellabban AM; Ali OS; Mohamed BA “Assessment of amniotic and polyurethane membrane dressings in the treatment of burns.” Burns – 01-AUG-2010; 36(5): 703-10.
- Huiren Tao & Hongbin Fan “Implantation of amniotic membrane to reduce postlaminectomy epidural adhesions.” Eur Spine J – 01-AUG-2009; 18(8): 1202-12. (). 2009.
- Arora R; Mehta D; Jain V “Amniotic membrane transplantation in acute chemical burns.” Eye (Lond). (19)3. 01-MAR-2005. pp 273-8.
- Kay H; Nelson D; Wang Y. “The Placenta: From Development to Disease.” Wiley-Blackwell. 2011.